HW#34 Ch 13: Gravitation
Instructions: Be sure to write formulas and show substitutions to earn full credit.
1. A gravimeter is an instrument used to measure the local gravitational field, which is expressed in gals, defined as 1 cm/s2. Valia brings a gravimeter to the top of Mauna Loa, which has a maximum elevation of 4170 m and a density of 2,670 kg/m3.
a) The free air correction takes account of the fact that higher elevations are further from the center of Earth. How much lower is Valia's gravity reading at the top of Mauna Loa than the reading at sea level? Express her answer in milligals and consider only the distance from the Earth’s center and the mass of the Earth.
b) The Bouguer correction takes into account that there is extra mass above sea level. Assume that there is a shell of thickness H that is added to a spherical Earth (above sea level). Show that the gravity reading will be higher by an amount 4πGρH, where ρ is the density of the shell and H << R. (You will need to use a binomial approximation.)
c) How much higher is Valia's gravity reading due to Bouguer correction? Express the answer in milligals.
d) Which represents the greater deviation, the free air correction (part a) or the Bouguer correction (part c)?
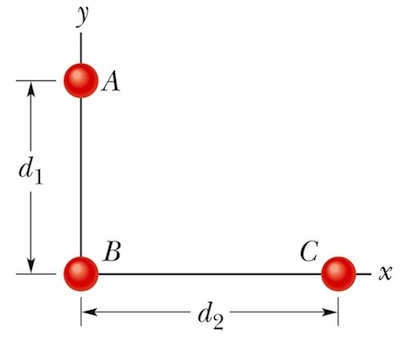
2. In the figure below, three particles are located at distances d1 = 2 m and d2 = 3 m. If each particle has a mass of 2 kg, what are (a) the magnitude and (b) the direction (angle relative to the x axis) of the net gravitational force on sphere B due to spheres A and C?
3. How far above Earth’s surface will the acceleration of gravity be 90% of the surface value?
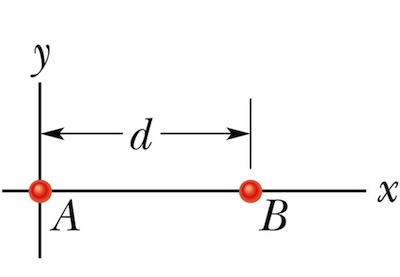
4. In the figure below, two balls are fixed on the x-axis separated by a distance d = 5 m. Ball A has a mass of 3 kg and ball B has a mass of 5 kg. A third ball C, of mass 6 kg, is to be placed on the x axis near particles A and B. At what x coordinate should C be placed so that the net gravitational force on ball C from balls A and B is zero?